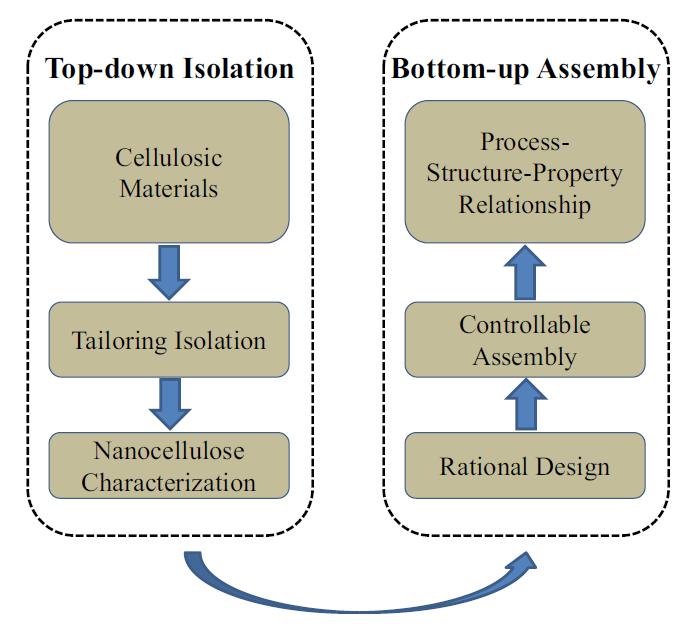
Various types of nanocellulose have been isolated from the cellulosic feedstock. It was expected that nanocellulose could be used to replace fossil-based plastic in certain areas because it is biodegradable, biocompatible, environment-friendly, and has outstanding performance. Unlike conventional plastic processing, nanocellulose is generally isolated and processed in aqueous environments. Therefore, dewatering and drying are essential unit operations for nanocellulose processing. Different drying methods for colloidal nanocellulose suspension mediated different self-assembly behaviors and thus resulted in different nanocellulose morphology and physical properties. The most utilized techniques for nanocellulose processing, such as spinning, vacuum/pressurized filtration, solvent casting and roll to roll casting, coating and roll to roll coating, and additive manufacturing are investigated. Process parameters such as temperature, pH, ion species, concentration, and
external electrical field, affect the orientation and assembly behavior of nanocellulose, which in turn influence the properties of the prepared materials. Therefore, the method for assembling nanocellulose into bulk materials in a controlled way is vital for the properties of the fabricated nanocellulose composites. Here, some of the recent advances in the processing of nanocellulose for bulk materials are reviewed.