Enzymatic reduction of graphene oxide by a secreted hydrogenase
Although reducing graphene oxide (GO) is a promising method for producing graphene, it involves high energy consumption and serious pollution. Here, an eco-friendly and cost-effective method to reduce GO was developed, in which GO was reduced by a fermentation-medium system containing self-secreted [FeFe]-hydrogenase (CFM-H2ase). It was found that GO could be rapidly reduced by hydrogen which was catalyzed by the fermentation medium of Escherichia coli that heterologously expressed [FeFe] hydrogenase. The reduced GO nanosheets were characterized and confirmed by Raman, XRD, and XPS analysis, which indicated a high reduction ratio was achieved. Further analysis revealed that the [FeFe] hydrogenase secreted by the genetically engineered E. coli cells was responsible for the catalysis of hydrogen-induced GO reduction, which was the underlying mechanism for GO reduction by the CFM-H2ase system. This work demonstrated a new enzymatic approach for GO reduction, which would be helpful in developing a more sustainable graphene industry
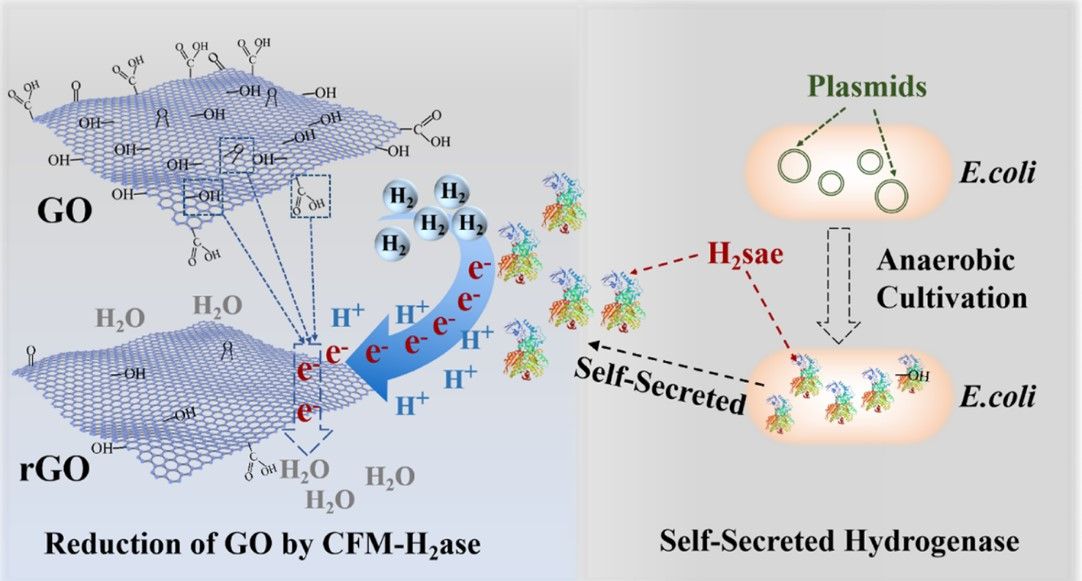
Schematic for designed new CFM-H2ase route for GO reduction
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2024.109220